
We were also limited to only writing to the source drive. The RSYNC solution was the simplest, but it took 10 minutes for changes to show up and RSYNC put so much load on the servers we had to throttle it with custom script to pause it every second. A shared SAN drive running OCFS2 mounted both servers.A central CIFS (SAMBA) share to both servers.Local drives on each server synced with RSYNC every 10 minutes.The table below lists the transport protocol in the "Transport" column.We have a 2 server load-blanacing web cluster.We have tried the following methods for syncing content between the servers: IANA devotes each port number in the registry to a specific service with a specific transport protocol. The column "Assigned by IANA" indicates whether the port is listed in the Service Name and Transport Protocol Port Number Registry, which is curated by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). The control port is the port used for the dialogue of commands and status updates between client and server. In the table below, the data port is the network port or range of ports through which the protocol transmits file data. ^ The BNU implementation of UUCP can resume an interrupted file transfer.
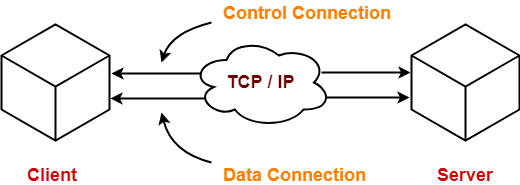
^ These are the options in the reference implementation, which uses OpenSSL.^ It's recommended to use HTTPS provided by a webserver, proxy, or SSL terminator.RFC 3659 (2007) provides for resuming in stream mode. ^ RFC 1123 (1989) extends and corrects the provisions for restart/resume that were published in RFC 959 (1985).^ One implementation, Fujitsu openFT, applies AES.^ RFC 6726 suggests IPSec as one option.^ Some implementations can obfuscate traffic using RC4 et al.Tus open protocol for resumable file uploads ( tus) Simple Asynchronous File Transfer ( SAFT) Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol ( S-HTTP) NACK-Oriented Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol (NORM) Protocolįile Delivery over Unidirectional Transport ( FLUTE)įile Transfer Access and Management ( FTAM) Such protocols may be preferred for electronic data interchange. MFT protocols prioritise secure transmission in industrial applications that require such features as auditable transaction records, monitoring, and end-to-end data security. The "Managed" column indicates whether the protocol is designed for managed file transfer (MFT). Tus open protocol for resumable file uploads IETF Web Transaction Security Working Group Organisation for Data Exchange by Tele Transmission in Europe NACK-Oriented Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol Ludvig Strigeus, Greg Hazel, Stanislav Shalunov, Arvid Norberg, Bram Cohen Overview Color key: International standard Internet Standard Proposed Standard Internet Draft Protocolįile Delivery over Unidirectional Transport Similarly, the encryption scheme indicated in the "Encryption" column applies to transmitted data only, and not to the authentication system. Some protocols-including FTP, FTP Secure, FASP, and Tsunami-listen on a "control port" or "command port", at which they receive commands from the client.
In the case of FTP, this port differs from the listening port. The " Server port" column indicates the port from which the server transmits data. Some protocols designed to transmit data over UDP also use a TCP port for oversight. In the tables below, the "Transport" column indicates which protocol(s) the transfer protocol uses at the transport layer. They use one of two transport layer protocols: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The Internet is a packet-switched network, and most of the protocols in this list are designed for its protocol stack, the IP protocol suite. A packet comprises a header (which describes the packet) and a payload (the data). Protocols for packet-switched networks Ī packet-switched network transmits data that is divided into units called packets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
